What is SAP Business One? Maybe you’ve asked this when discussing it with your friends working in other companies. Or when you ask for advice on what ERP system is suitable for your company. You are not alone, and many people still do not know or even hear about SAP B1.
SAP (System Application and Product in data processing) is a software or software that provides complete modules interconnected/integrated to help manage business management from small, medium, to large scale.
This SAP Business One solution is known as one of the world-class ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems that aims to help simplify business processes and automate essential business functions in finance, opportunity and sale, purchase and supply chain, production planning and inventory control, project management, and analysis and business intelligence.
With complete information, you can make decisions quickly and accurately based on real-time information and, in the end, will be able to help increase your business profits.
Before we discuss in more detail about SAP B1, let’s look at its history first.
SAP Company History
The SAP company was founded on April 1, 1972, with its head office in Walldorf – Germany. The company was founded by five people who previously worked at IBM:
- Dietmar Hopp
- Hasso Plattner
- Hans-Werner Hector
- Klaus Tschira
- Claus Wellenreuther
The first time the system was built and marketed in 1973 was only a system for Financial Accounting. However, as time goes on, each module is added to become a complete unit and is integrated. And further develops:
- R/2 in 1982
- R/3 in 1993
- SAP All-in-One and SAP B1 in 2006
- SAP Business ByDesign in 2007
- SAP Hana, which was a database platform in 2011
- SAP S/4Hana in 2015
History of SAP Business One
SAP Business One was initially launched in 1996 under the name “Menahel,” or in Indonesian means “Manager,” and was launched to European and Latin American markets under the name “TopManage” in 2000. At that time, “Menahel” or “to manage” is not owned by SAP yet.
In 2002 SAP bought “TopManage” and changed its name to “SAP Business One.” With this system, SAP can better reach small companies that previously could not afford to buy an SAP system.
Main Functions of SAP Business One
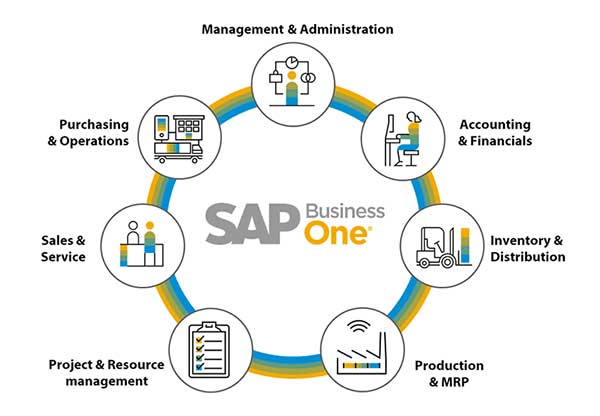
Although it is intended for use in small and medium-sized companies, the functions and features provided in SAP B1 are quite complete:
- Administration, this function is used to set up the core of the SAP B1 application.
- CRM is used to record and integrate the activities of the sales team with other modules.
- Financial includes the setup and configuration of the Chart of Accounts and the creation of manual journals for financial and accounting purposes.
- Opportunities, a function used in the lead generation process by recording potential sales and purchases.
- Sales – A/R, to manage & record the sales process starting from the Bidding process – Sales Orders – Delivery – to Billing to customers/customers.
- Purchasing – A/P, to manage & record the purchase process starting from the Bid process – Purchase Order – Receipt of goods – up to Billing from the seller/supplier.
- Business Partner, a module used to record master data of prospects, customers, and suppliers.
- Banking records payment processes to suppliers or receipt of customer payments.
- Inventory is a module used to store master data of goods and record stock and transactions for moving or entering goods.
- Resources, a module used to record master data of resources (machines or labor) used in the production process.
- Production, including master data recording for Bill of Materials and production orders. This includes the use of materials and receipt of finished goods produced.
- Project Management, a module used to make it easier for you to manage and monitor your projects.
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP) helps plan the needs of goods in the sales/production process.
- Service, a module used for service contract management, such as service for electronic goods using a warranty card.
- Human Resources, a module that is used only to store employee master data information.
Although each module has its use and function, each SAP Business One module is integrated.
And the advantage of SAP Business One is that you can easily see the relationship between documents.
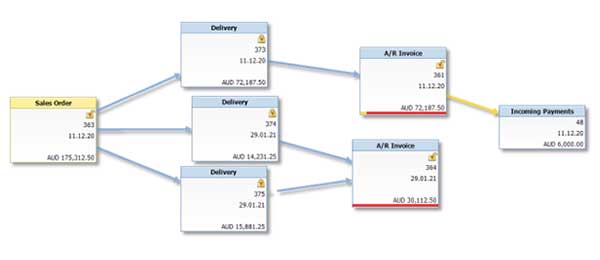
This, of course, will significantly facilitate your staff or audit team in tracing a process or document.
With the existing functions, it can be said that SAP B1 is specially designed for your business when viewed from various aspects:
- Complete – All important business (accounting, customer relationship management (CRM), operations, sales, marketing, service, warehousing, etc.) into one out of the box. Complete functions and better control help you professionally run your business processes.
- Combination – All business functions are contained in one package, which makes them easy to create, use, and optimize. Integration with other systems is a standard integration package or an open application programming interface (API).
- Spacious – A flexible platform with 50 localizations and 28 languages. Over 500 pre-integrated, industry-specific and horizontal solutions, all available through SAP partners.
- Innovation – Offered via mobile devices and provides real-time data.
- Affordable – You can start with a basic on-premise implementation with multiple users. Or use the starter package**, which includes software and implementation, a cheaper, faster, low-risk option with limited capacity for up to five users. A cloud solution is available for a monthly fee.
Sap Business One Investment / Pricing
SAP Business One is business management or ERP software for small to medium-sized businesses. Every business process certainly requires special care and attention so the business can run smoothly and succeed. For business processes to run efficiently, not a few entrepreneurs have adopted the SAP program so that they can help every step of the process.
Several components must be calculated in the implementation of SAP B1:
- SAP B1 License
The number and type of licenses used are determined based on the number of users who will use the system and the roles of each of these users. - Implementation
Several components influence the length of time and cost of implementation:- Business process complexity
- Number of master data
- Number of users
- Server and other supporting hardware
The Advantages of SAP Business One
SAP B1 is an intelligent solution that provides several advantages:
Can be accessed using any device and from anywhere
This application is relatively easy to use and flexible. You can access it anytime and anywhere, using any device. SAP system can be operated using Microsoft SQL Server database or using SAP Hana
Supporting Business development
Using SAP software also supports your business that wants to be developed abroad. This can be seen with the service of up to 27 languages in 43 countries.
Able to meet the changing needs of the Company
When your business grows, this system can make it easy to adjust and expand the use of the SAP program according to your Company’s business changes.
Thus, the investment costs incurred for implementing SAP B1 will be proportional to the results obtained later.
Implementation of SAP Business One
Because it is intended for small and medium-sized companies, the process of implementing SAP Business One is not too complicated and not too time-consuming as in the implementation of SAP S4/Hana. But what is certain, the need for cost and implementation time depends on several factors such as the number of users, the amount of data, and the complexity of the business process.
For example, in retail companies, the number of users of the SAP B1 system is usually insignificant. Still, the complexity of the retail business in Indonesia and the vast amount of data items (which can reach hundreds of thousands to millions) affect the implementation time requirements.
Because usually, when companies plan to use a new system, they want the data that has been used so far to be cleaned up. Example:
- Item code naming has been tidied and uniformed.
- Items that are out of stock are no longer used.
- The categorization of goods has been adjusted again to generate reports as needed.
In manufacturing companies, usually, the determinant is the number of users and the complexity of the business process.
It’s another thing for distribution/trading companies, where one aspect that influences is the number of customer data that can reach thousands.
Several important stages in the SAP Business One implementation process are:
- Project preparation
Provide understanding to the entire project team regarding each user’s cooperation, commitment and responsibility. - Business process blueprint
Consultants and users discuss ongoing business processes and what things can be improved or adapted to the SAP B1 system. - Realization
During the ” Business Blueprint ” phase, the configuration, development, training, and testing process is done by the agreed business processes during the “Business Blueprint” phase. - Final preparation
Final preparations for the new go-live system, including finalizing master data, cut off strategy. - Go Live and Support
But in the process, we often hear that companies can use the existing system successfully, but not other companies, even though both use the same system and have the same business processes.
From some data we have tried to collect from 1994 – 2015, the success rate of a system implementation for 20 years is only in the range of 20% – 35%.
This is surprising because it means that there is only one successful project from every 3 to 5 ERP system implementation projects.

SAP implementation is not easy. Companies that want to use this application need help and guidance from parties who have worked with SAP. Both already have the category as SAP Gold Partner and those who have the category as SAP Premium Partner.
From the inner side of the company itself, the difficulties experienced can be in the form of:
- Adjustment of business processes with functions and features available in SAP applications.
- There are conflicts or problems with certain parties.
- Corporate culture is hard to change.
From our experiences in implementing SAP B1 in customer companies, several things are the main keys to the success of implementing SAP Business One, namely:
- Support from executive management / top management
- Traps of hope/expectations
- Business process blueprint
- Data preparation management
- Training
- Testing
- Readiness of prospective users (users)
- Go-Live Strategy – Parallel Run Vs Cut Off
According to their activities and interests, these critical points are in each implementation stage.
Types of Industry Using SAP
SAP B1 is an ERP system solution built globally by SAP for all types of industries. However, each industry must have its unique business process, be it the retail industry, the manufacturing industry, the distribution or trading industry, the automotive industry, or even the commodity and livestock industries.
That is crucial in choosing an SAP Business One partner. You must be able to see and analyze carefully which partners can be able to provide solutions and become friends in discussions during the implementation process.
The more the consultant focuses on a particular industry, the more mature the solution will be.
PT Sterling Tulus Cemerlang, as SAP Gold Partner focuses on four industries, namely:
- Manufacturing
- Distribution/Trading
- Retail
- Commodities & Livestock
How SAP B1 can help companies in Indonesia in managing their business can be seen in the following video:
Information about companies that have used SAP B1 can be found here client STEM.


