RPA or Robotic Process Automation is the technology that allows computer software to mimic actions typically performed by humans interacting with digital systems to perform simple, repetitive tasks and business processes.
RPA is not a physical robot like the ones we encounter in the production process or a robot that can walk and talk like humans. RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is software that can help us complete work done on digital systems (computers or mobile devices). RPA mimics mouse clicks and keyboard taps to complete the work process.
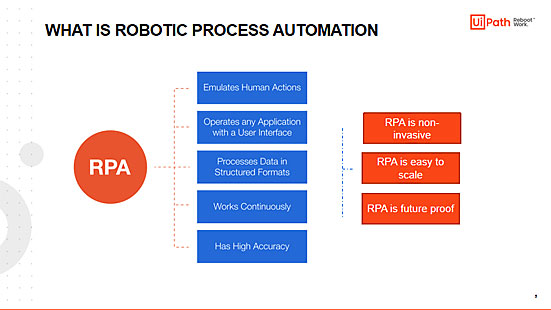
What does RPA do?
- RPA Emulates Human Actions
- Robotic Process Automation Operates any Application with a User Interface
- Processes Data in Structured Formats
- Works Continuously
- Robotic Process Automation Has High Accuracy
Characteristics of the RPA
RPA is non-invasive
It does not require any major IT architecture changes or deep integration with the underlying systems. RPA offers a reliable, fast and cost-efficient solution for a “light-weight” integration into processes and IT assets.
RPA is easy to scale
The amount of work involved in a process can vary, as changes are likely to occur in most business environments. If an RPA solution is used, companies can easily adapt by scaling the solution up or down, depending on the requirements.
Robotic Process Automation is future proof
Robots work with today’s technology, yet the automation is extensible, able to handle tomorrow’s technology.
UiPath Demo – Sales Data Transfer from IREAP POS Report to SAP Business One AR Invoice
What Processes Should Be Automated by RPA?
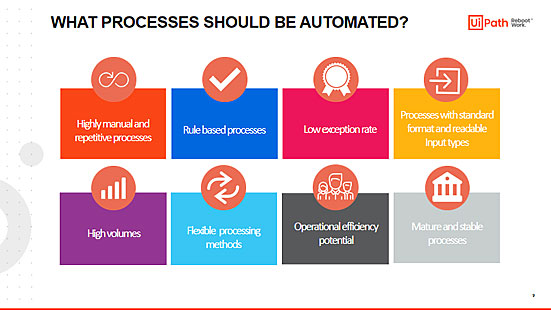
But what qualifies processes for automation using Robotic Process Automation?
Essentially, any high-volume, business-rules-driven, repeatable process qualifies for automation.
1. Highly manual and repetitive processes
These are high transaction volume processes, highly frequent processes running daily & weekly, instead of monthly or yearly which involve high manual work or work prone to human error.
2. Rule-based processes
Activities with clear processing instructions with decision making based on standardized and predictive rules.
3. Low exception rate
Activities with a low number of various scenarios existing in the process leading to different handling procedures.
4. Processes with standard readable electronic input type
Processes triggered by standard and consistent inputs. These inputs should be in a readable input type like Excel, Word, email, XML, PPT, readable PDFs etc. Processes triggered by input types that are not readable like images scanned without OCR are not disposed to automation.
5. High volumes
Processes with high transaction volumes and high frequency.
6. Changeable processing method or system change
Processes for which the processing method cannot be changed due to various reasons and do not require a fundamental change in the underlying technical architecture of the current systems. We strongly recommend avoiding automation in processes for which changes are expected in the short/medium term.
7. Operational efficiency potential
Our recommendation is to automate only those processes which can provide savings in terms of human work-effort of a minimum of 2 full-time employees or FTEs.
8. Mature and stable processes
Processes that tend to be well documented, stable & predictable with well-known operational costs.
Examples of Typically Automated Business Processes with RPA
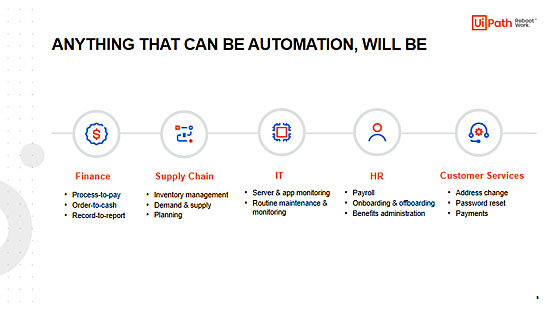
The true value of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is realized when humans and robots are each focused on the tasks for which they are best suited.
Let’s now look at a few industries and the common processes where RPA is being deployed.
- Finance Departemen
- Process-to-pay
- Order-to-cash
- Record-to-report
- Supply Chain Departemen
- Inventory management
- Demand & supply
- Planning
- Human Resource Departemen
- Payroll
- Onboarding & offboarding
- Benefits administration
- Information Technology Department
- Server & app monitoring
- Routine maintenance & monitoring
- Customer Services Department
- Address change
- Password reset
- Payments
Take a moment to review the areas where automation can have the biggest impact across finance, supply chain, IT, Human resources, and Customer Service.
As you can see, automation opportunities are everywhere.
For more information on how Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and UiPath can help your company become more efficient, please contact PT. Sterling Tulus Cemerlang CONTACT US
UiPath Indonesia Demo Document Extraction – Download Email PDF and Enter into SAP Business One Sales Order

